Memo / Windows registry
21 Jun 2020Explanation
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Windows OS and applications using the registry. This is a brief summary of How it is and how to browse / edit it.
Opening with regedit.exe
First, open the registry with regedit.exe. We have 5 root keys there.
1. HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT(HKCR)
- A section to manage file type associations.
- Provides a view of the registry that merges the information from
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\ClassesandHKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classes. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classesholds default settings that can apply to all users on the local computer.HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classeskey contains settings that override that default settings.
2. HKEY_CURRENT_USER(HKCU)
- Information about the user currently logged in.
HKCU\Softwareholds user-level settings for the most of the software.%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Usrclass.datand%LocalAppData%\Microsoft\Windows\Usrclass.dathold the data.
3. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE(HKLM)
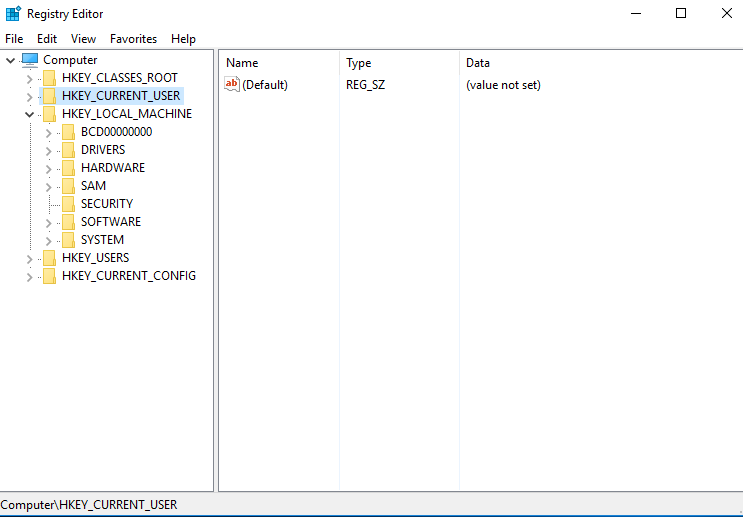
- Majority of the configuration information for the software we install and Windows operating system itself.
BCD00000000
- Boot configuration Database.
- Replaced
boot.iniof Windows XP
HARDWARE
- Holds data pertaining to the BIOS, processors and other hardware devices.
SAM
- Database for Security Accounts Manager. Need SYSTEM account to access.
- Stored in
%SystemRoot%\System32\Config\SAM
SECURITY
- Need SYSTEM account to access.
- Stored in
%SystemRoot%\System32\Config\SECURITY
SOFTWARE
- Most commonly accessed from the HKLM hive. Organized alphabetically by the software vendor.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classessubkey of this key describes various UI details including extensions.%SystemRoot%\System32\Config\SOFTWARE
SYSTEM
- Stored in
%SystemRoot%\System32\Config\SYSTEM.
4. HKEY_USERS(HKU)
- Stores all of the settings for all user profiles actively loaded on the system.
5. HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG(HKCC)

- Information about the hardware profile that is used by the local computer at system setup.
Stored data type
These are the examples of the stored data type of Windows registry.
- REG_BINARY : Binary value.
- REG_DWORD : DWORD (32bit), used for a regular integer value.
- REG_QWORD : QWORD (64bit), used for a 64-bit integer value.
- REG_SZ : String value.
- REG_EXPAND_SZ : String that can contain environment variables, often used for system paths.
- REG_MULTI_SZ : Multiple string used to represent values that contains lists or multiple values, separated by a NULL character
- REG_RESOURCE_LIST : Series of nested arrays that is designed to store a resource list used by a hardware device driver or one of the physical devices it controls.
- REG_LINK : A Unicode symbolic link.
- REG_NONE : No defined type value.
How to get SID of users
1. Get SID of a local user
C:\Users\Administrator>wmic useraccount where name='Administrator' get sid
SID
S-1-5-21-299884335-592523710-3968369954-500
2. Get SID for current logged in domain user
C:\Users\Administrator>whoami /user
USER INFORMATION
----------------
User Name SID
====================== ===========================================
mydomain\administrator S-1-5-21-299884335-592523710-3968369954-500
Browse Windows registry with command prompt
1. Listing subkeys
C:\Users\Administrator>reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows"
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\ClickNote
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\DWM
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\EnterpriseResourceManager
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\HTML Help
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\ITStorage
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\ScheduledDiagnostics
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\ScriptedDiagnosticsProvider
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Shell
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\SoftwareInventoryLogging
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\StreamProvider
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Tablet PC
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\TabletPC
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Search
2. Extract a specific value of a key
C:\Users\Administrator>reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RUN" /v VBoxTray
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RUN
VBoxTray REG_EXPAND_SZ %SystemRoot%\system32\VBoxTray.exe
Browse / Edit Windows registry with PowerShell
1. Listing all exposed drives including HKLM and HKCU
PS C:\Users\Administrator> get-psdrive
Name Used (GB) Free (GB) Provider Root CurrentLocation
---- --------- --------- -------- ---- ---------------
Alias Alias
C 16.14 33.37 FileSystem C:\ Users\Administrator
Cert Certificate \
D 0.06 0.00 FileSystem D:\
Env Environment
Function Function
HKCU Registry HKEY_CURRENT_USER
HKLM Registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
Variable Variable
WSMan WSMan
2. Navigate to the local machine registry root key
We can use cd command.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> cd HKLM:\
PS HKLM:\>
Or we can use Set-Location for PowerShell.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> set-location -path HKLM:\SOFTWARE
PS HKLM:\SOFTWARE>
3. Output sub keys
PS HKLM:\SOFTWARE> Get-Childitem
Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE
Name Property
---- --------
Classes
Clients
Intel
Microsoft
ODBC
Oracle
Partner
Policies
RegisteredApplications File Explorer :
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Capabilities
Internet Explorer : SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Capabilities
Paint :
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Paint\Capabilities
Windows Address Book : Software\Clients\Contacts\Address Book\Capabilities
Windows Disc Image Burner : Software\Microsoft\IsoBurn\Capabilities
Windows Media Player : Software\Clients\Media\Windows Media Player\Capabilities
Windows Photo Viewer : Software\Microsoft\Windows Photo Viewer\Capabilities
Windows Search : Software\Microsoft\Windows Search\Capabilities
Wordpad :
Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Wordpad\Capabilities
4. Output registry entries in a readable form
PS HKLM:\> Get-ItemProperty -path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
ProgramFilesDir : C:\Program Files
CommonFilesDir : C:\Program Files\Common Files
ProgramFilesDir (x86) : C:\Program Files (x86)
CommonFilesDir (x86) : C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files
CommonW6432Dir : C:\Program Files\Common Files
DevicePath : C:\Windows\inf
MediaPathUnexpanded : C:\Windows\Media
ProgramFilesPath : C:\Program Files
ProgramW6432Dir : C:\Program Files
SM_ConfigureProgramsName : Set Program Access and Defaults
SM_GamesName : Games
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVer
sion
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
PSChildName : CurrentVersion
PSDrive : HKLM
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
5. Add a new key
PS HKCU:\> new-item 'HKCU:\Testkey'
Hive: HKEY_CURRENT_USER
Name Property
---- --------
Testkey
6. Add a new property to a key
PS HKCU:\> new-itemproperty -LiteralPath 'HKCU:Testkey' -Name 'param1' -PropertyType 'String' -Value 'test'
param1 : test
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Testkey
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER
PSChildName : Testkey
PSDrive : HKCU
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
7. Retrieve properties from a key
PS HKCU:\> Get-ItemProperty -path HKCU:\Testkey
param1 : test
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Testkey
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER
PSChildName : Testkey
PSDrive : HKCU
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
8. Retrieve a value of single property from a key
PS HKCU:\> Get-ItemPropertyvalue -LiteralPath 'HKCU:Testkey' -Name param1
test
9. Update a value of single property
PS HKCU:\> set-itemproperty -Literalpath 'HKCU:Testkey' -Name param1 -Value 'test-test'
PS HKCU:\> Get-ItemPropertyvalue -LiteralPath 'HKCU:Testkey' -Name param1
test-test
10. Existing check of a key
PS HKCU:\> Test-Path -LiteralPath "HKCU:\testkey"
True
11. Delete a key
PS HKCU:\> Remove-Item -LiteralPath "HKCU:\Testkey"
PS HKCU:\> Test-Path -LiteralPath "HKCU:\testkey"
False